Since the beginning, we only used high-quality materials: from common polymers, such as nylon, polypropylene, and polycarbonate, to the most innovative materials like Ecowood, PLA, and PEEK.
There is a wide range of materials suitable for injection moulding. In addition, polymers can be combined with one or more other elements to improve strength or aesthetics.
The choice falls on one material accordingly to the technical features and function of the final product. Each material has properties that determine specific moulding parameters.
MORE TECHNICAL INFORMATION
We work with the following materials
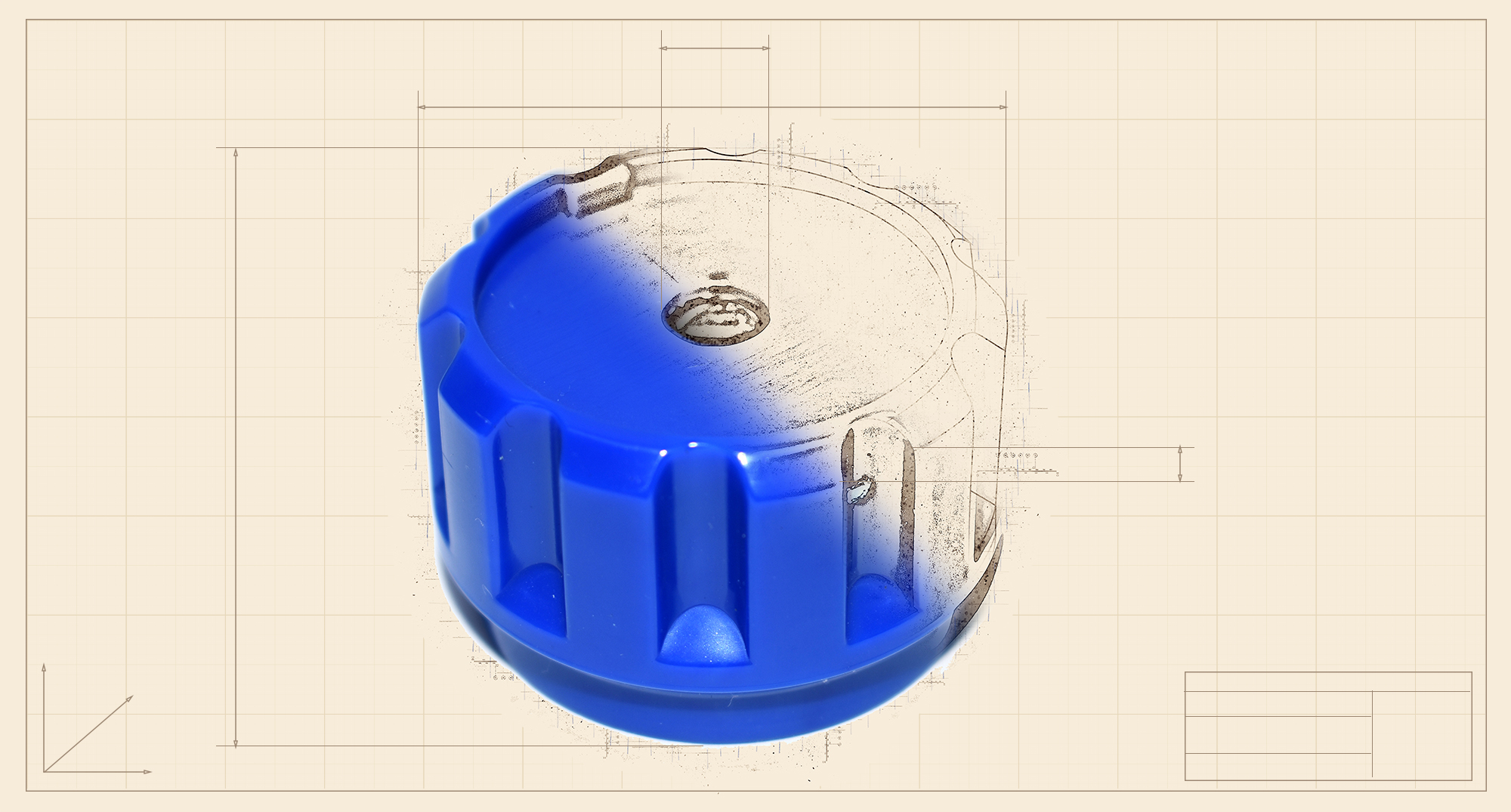
ABS (Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene)
ABS is a strong and impact-resistant thermoplastic polymer that finds applications in several industrial sectors. It has a low shrinkage ratio, high dimensional stability and is also quite economical. ABS prototype parts tend to develop weld lines and may present depressions and sink marks in thicker areas. We use a PC/ABS composite material to reduce depressions.
Products: valves for thermohydraulic, components for smart home appliances
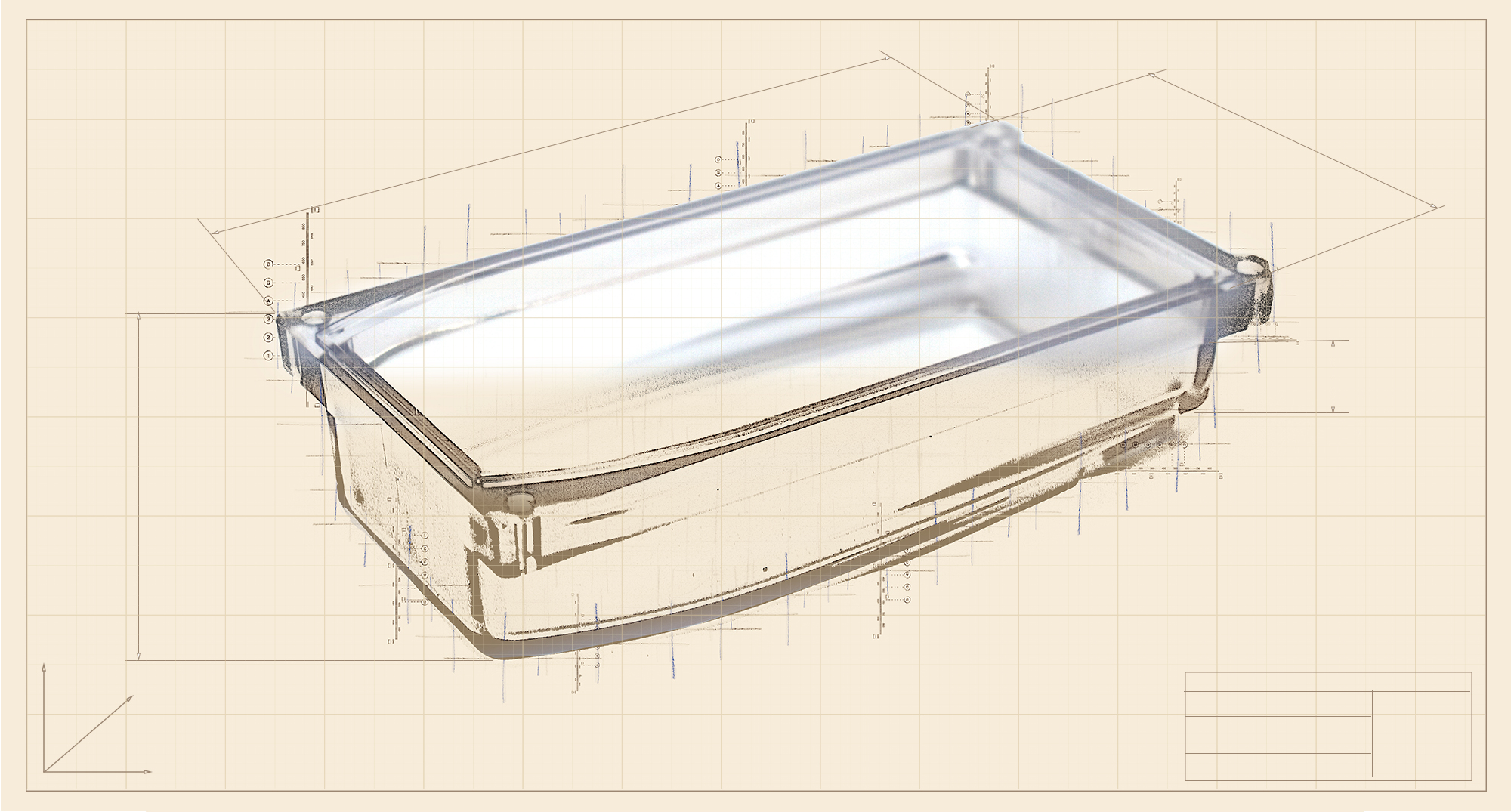
PC (Polycarbonate)
PC is a strong and extremely shock-resistant thermoplastic polymer It has a low shrinkage ratio, good dimensional stability and is available in different degrees of transparency. Additionally, PC has a good heat resistance and a wide range of aesthetically pleasing finishes. However, parts made with PC may appear flawed in thicker sections (sink marks, vacuum voids, and depressions). . This material has poor chemical resistance. Alternatively, for optimal performances, there are some PC/ABS blends on the market.
Products: electrical components, medical devices.
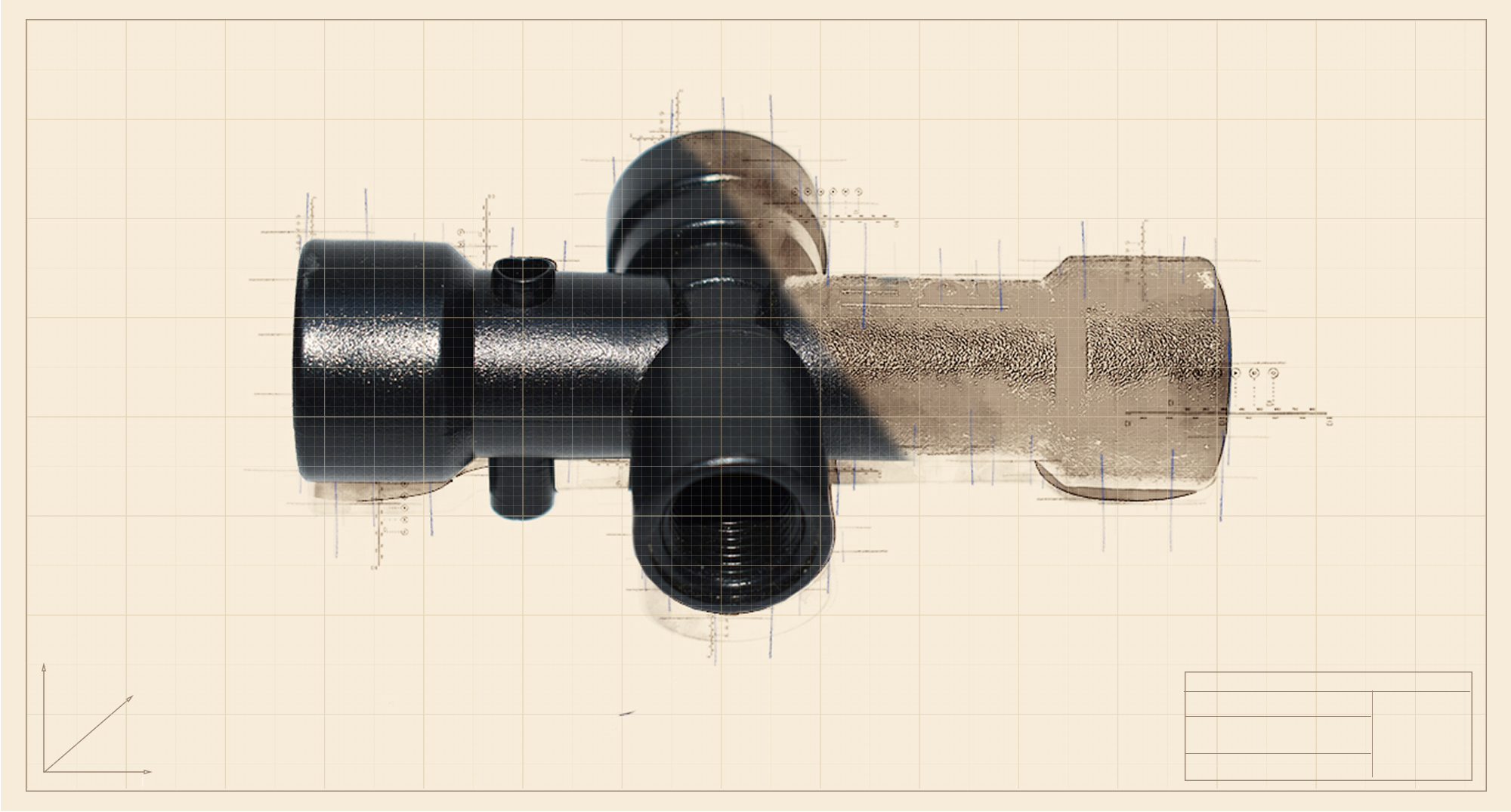
POM (Polyoxymethylene)
Polyoxymethylene (also known as acetal) is an engineering thermoplastic used for parts that require a high tenacity, stiffness, hardness, and strength. Acetal has excellent elasticity and slipperiness, good lubricating properties and resistance to hydrocarbons and organic solvents. However, POM is difficult to dye and not aesthetically pleasing. Moreover, this material tends to shrink quite easily. Therefore, we use it for parts with a uniform thickness.
Products: gears, pumps and impellers, conveyor belts, soap dispensers, fans and fan blades, car switches, components for electrical switches, buttons, and knobs.
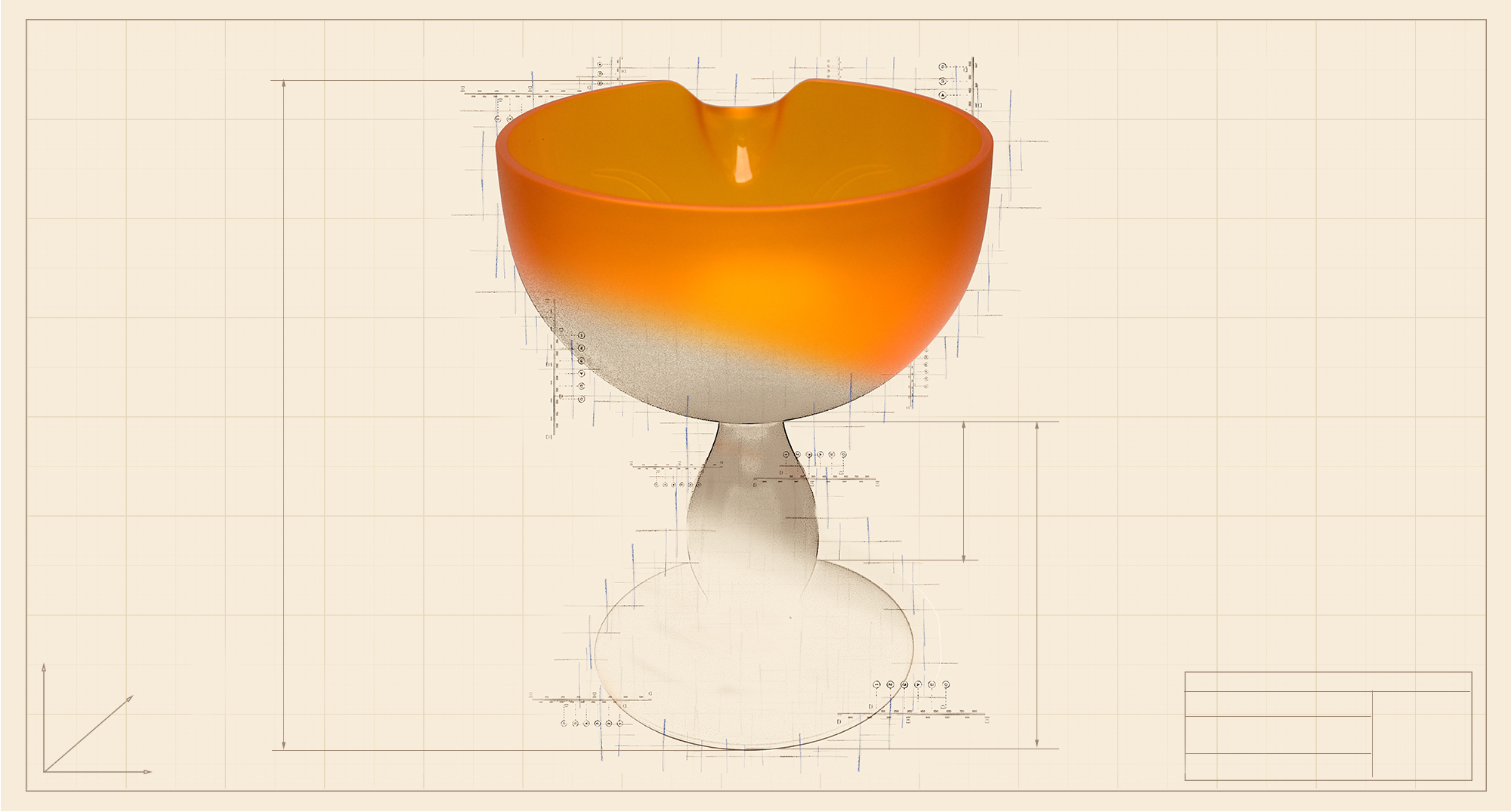

PMMA (Polymethylmethacrylate)
PMMA (also known as acrylic) is a scratch-resistant transparent thermoplastic with good optical properties but little chemical resistance.
The low shrinkage ratio makes PMMA the perfect candidate for parts with an uneven thickness (avoiding the development of depressions).
PMMA is also quite fragile; therefore, it is necessary to incorporate a draft angle in the design.
Products: tubular lights, lenses, lampshades, optical fibres, signals
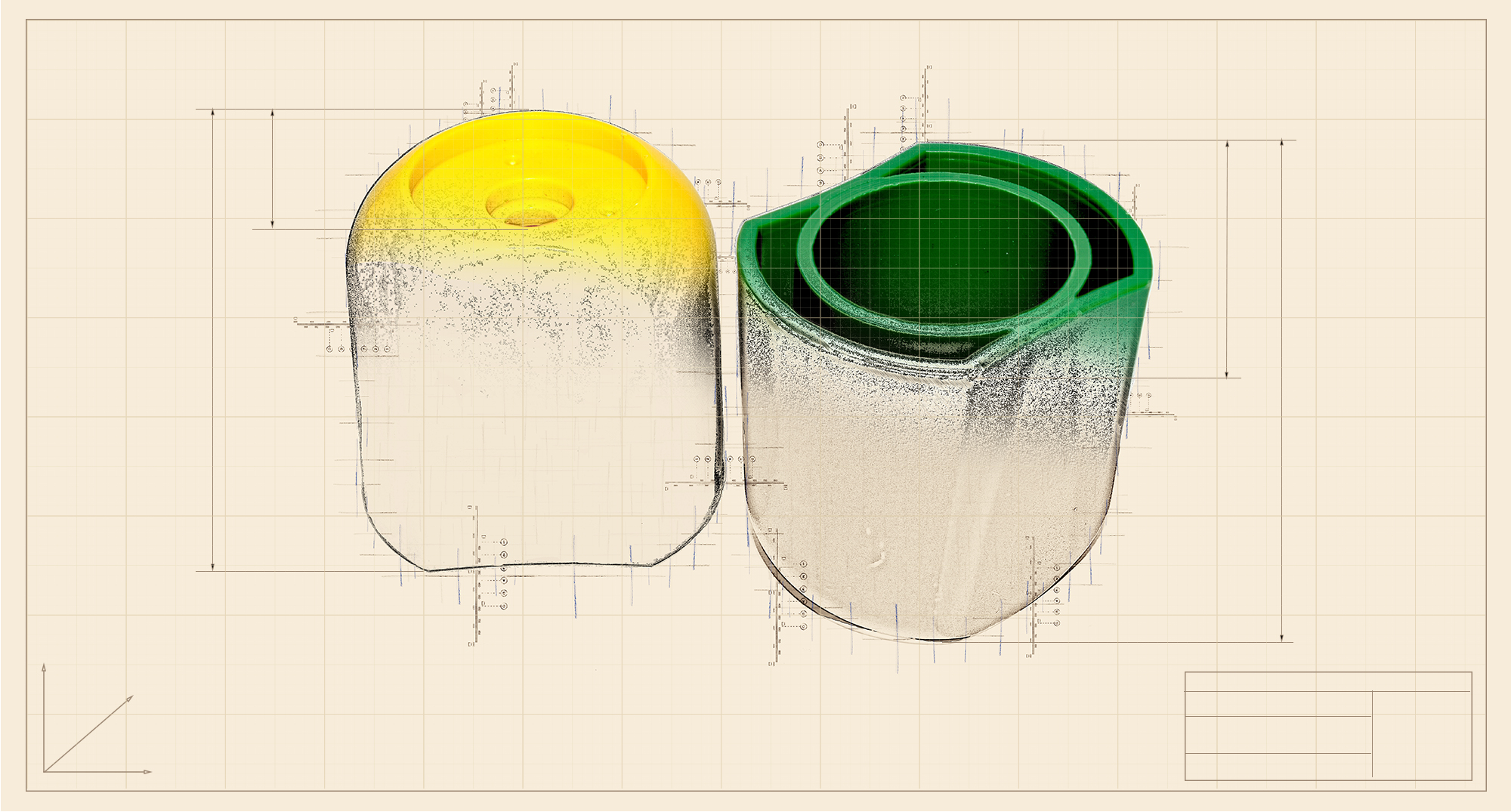
PP (Polypropylene)
Polypropylene is a durable, flexible, and cost-effective resin with a decent elasticity, good resistance to impact and good tolerance to acids and bases.
There are different types of PP: the homopolymer presents fragility at low temperatures; copolymers, on the other hand, are less fragile and more resistant to impact.
The most common production flaws are sink marks, vacuum voids, distortions, or suction marks.
Products: hand showers, cable drags, knobs
PBT (Polybutylene terephthalate)
PBT has a medium-high overall resistance and good tolerance to fuels, oils, fats, and many solvents. It does not absorb odours or flavours; therefore, PBT is suitable for applications in specific areas.
The good electrical and power properties of this material go hand-in-hand with the necessities of the automotive.
If reinforced with fibreglass, PBT tends to deform quickly and maintains less resistance from a chemical point of view.
Products: coffee machines and toasters, speakers, knobs and handles for electric hobs.
PPSU (Polyphenylsulfone)
PPSU is a type of high-performance polymer. It is a rock-hard material with a good heat and chemical resistance, both to weak acids/bases, and is also resistant to radiosterilization.
PPSU is suitable for high-temperature applications.
To avoid irregularities such as sink marks or vacuum voids, use this material for thin sections. Hydrocarbons and organic solvents usually attack this type of material.
Products: components for medical equipment, car fuse supporting structure, parts for aircraft interiors, fittings for hot water, lamp holders and connectors.
PEEK (Polytereterketone)
PEEK is a rather new material and finds applications in several areas.
Numerous elements make PEEK perfectly suited for the medical, aerospace, and automotive industry: good heat and chemical resistance, a slow combustion rate and excellent strength and dimensional stability. These high-performance features make this material quite pricey.
Products: electronic components

